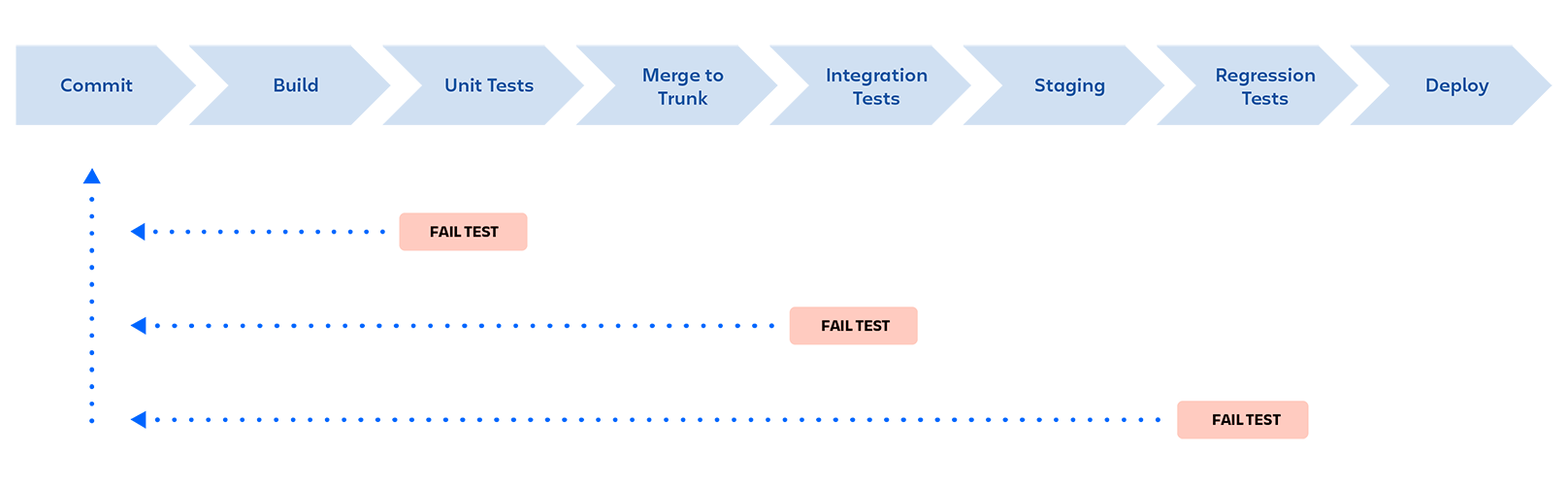
CI/CD Process
Trunk-Based Development is a key enabler of Continuous Integration and by extension Continuous Delivery.
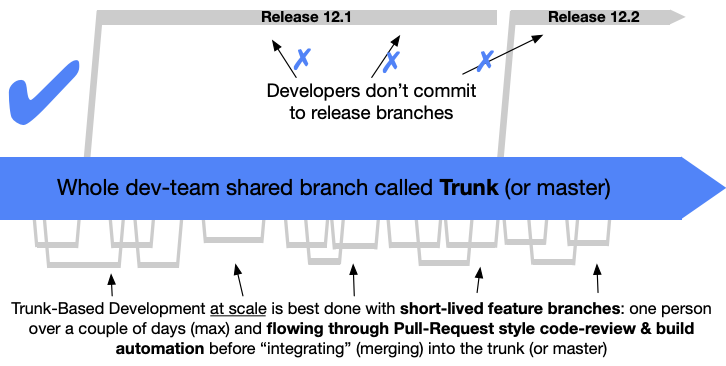
TODO: How will branches be determined? Feature flags? Branch by abstraction?
feature branches, fix branches, etc
Principles of Continuous Integration
Put source code into a version controlled mainline
- A minimally configured environment should be able to easily build, and run the product after cloning the repository
- It should be easy to find the code for a given piece of work
- The mainline is a single, shared branch that acts the current state of the product
Automate the build
- Anyone should be able to bring in a clean machine, check the sources out of the repository, issue a single command, and have a running system on their own environment.
Make the build self-testing
- Any programming task combines both modifying the functionality of the program, and also augmenting the test suite to verify this changed behavior
Everyone pushes commits to the mainline every day
Every push to mainline should trigger a build
- Utilize GitHub Actions
Fix broken builds immediately
Keep the Build Fast
- Set up a deployment pipeline
Hide work-in-progress
- Utilize keystone interfaces
Test in a clone of the production environment
Automate deployment
Principles of Continous Delivery
The product should always be in a state to release the latest build
Delivery is a collaborative effort (DevOps culture)
Automate of all possible parts of the delivery process, using a Deployment Pipeline
Deployment Pipeline
A deployment pipeline is an automated manifestation of your process for getting software from version control into the hands of your users.